Performance reviews are very important in the workplace. These processes are a valuable tool for human resource management because they help improve individual performance and contribute to the overall success of the organization. However, to be effective, the appraisal process must be fair, transparent, and based on objective criteria.
We provide a step-by-step explanation of how to conduct a job performance appraisal from a contemporary and agile perspective, without disregarding the fundamental theoretical principles.
Table of Contents
1. What is job performance appraisal?
Performance evaluation is a systematic and regular process that assesses how each worker demonstrates their professional skills, achieves their goals and aligns with corporate values or the responsibilities of their position.
This process is critical for companies of all sizes and industries. The success of all organizations hinges on their human resources, making it crucial to align each employee's individual development with the organization's developmental goals. To accomplish this, Human Resources departments employ performance evaluation, which enables them to implement continuous improvement initiatives and gather data for strategic decision-making.
An effective performance appraisal process facilitates proper talent management and exerts a very significant influence on the organization's culture, satisfaction and motivation of employees and general productivity levels.
*For a more detailed definition, please refer to the Performance Evaluation definition.
2. Benefits of Performance Reviews
Performance reviews help in many ways in the workplace because they provide a number of benefits to both employees and organizations. Here are some of the key benefits of performance reviews:
· Constructive feedback: It provides employees with feedback on their job performance, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement. This constructive feedback allows them to better understand their contributions and how they can grow professionally.
· Professional development: By identifying areas for improvement, employees can receive targeted training and development to strengthen their skills and competencies. This contributes to professional growth and career advancement.
· Motivation and recognition: This feedback process can also be used as a recognition tool. Recognizing and rewarding strengths helps motivate employees, promotes a positive work environment, and boosts morale.
· Set specific, clear, and measurable goals: These processes typically involve setting clear goals and expectations for employees. This helps align individual goals with organizational goals, improving efficiency and productivity.
· Make personnel decisions: Performance reviews are useful in making human resource management decisions, such as promotions, transfers, or salary adjustments. They provide objective data to support these decisions.
· Identify training needs: By assessing performance, organizations can identify training needs at the individual and collective levels. This facilitates the planning of specific training programs to improve the skills and knowledge of the team.
· Communicate effectively: Encourage open and honest communication between employees and managers. These regular conversations can strengthen working relationships, improve mutual understanding, and resolve potential problems before they become more serious.
· Alignment with overall goals: By evaluating performance, organizations can ensure that individual efforts are aligned with organizational goals and values, thus contributing to the overall success of the company.
3. Steps to carry out a performance evaluation
Conducting a performance review involves several steps to ensure an effective and fair process. Here is a general guide for you to follow:
3.1 Step 1: Choose the indicators to evaluate
The initial step involves determining which skills, tasks, knowledge, or objectives we intend to evaluate for each job role. We will gather these performance indicators for each Professional Profile, encompassing descriptions, potential levels of achievement, along with their corresponding scores, and specifying the minimum score necessary for the job role. Optionally, we may assign weights to the assessed indicators to factor into the result calculation.
After finalizing the indicators for each professional profile, the next phase is to construct survey templates for evaluating employees in their respective positions.
Here is an example of a survey for performance evaluation that can serve as a guide:
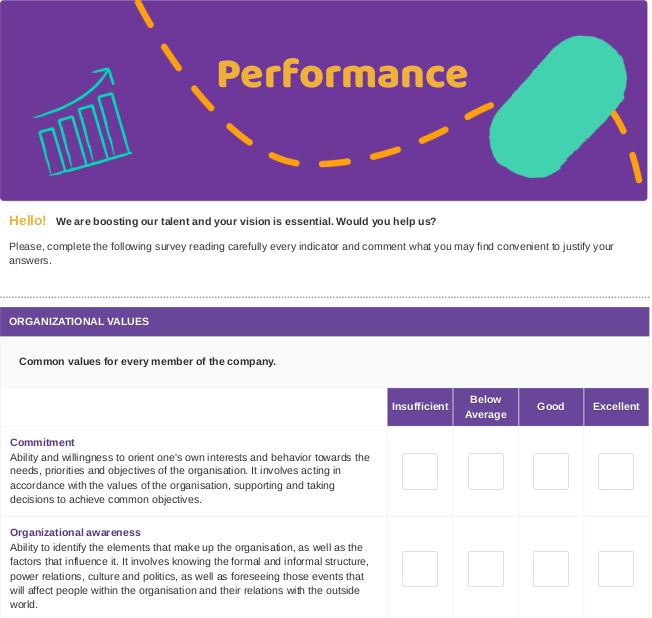
Next, we should design a performance evaluation system that provides us with the most comprehensive perspective. Let's explore the types of indicators we can assess to attain this objective:
-
Hard Skills & Soft Skills
Hard Skills refer to specific skills or technical knowledge required to perform particular tasks. These skills are typically acquired through academic training and professional experience. Examples include proficiency in a programming language or the operation of specific industrial machinery.
On the other hand, Soft Skills encompass competencies that encompass habits, behaviors, and approaches to working and interacting with our surroundings. Some of these skills include teamwork and the ability to handle pressure. In today's digital landscape, recognizing these competencies is crucial for ensuring the success and sustainability of our organization (for more details, see our post: Soft skills in the Fourth Industry Revolution).
-
Objectives & KPIs
We have all envisioned having a list of objectives that enables us to assess our employees' performance objectively without making things overly complicated. In some instances, it's relatively straightforward; for example, measuring the number of sales for a salesperson or BAIT for a financier. However, reality is often far more intricate than that. We require our employees to actively engage in defining and measuring the achievement of these objectives so that the evaluation accurately mirrors the workplace reality.
-
Organizational Values
Remaining aligned with organizational values is crucial for any organization. Consequently, incorporating these values into performance evaluations signifies the organization's commitment to them. When an employee observes, for instance, that integrity is included in the performance evaluation, it conveys the organization's dedication to upholding that value.
-
Others
There may be other elements that can be valuable in a certain context even if they are not directly related to the job. For example, proficiency in English or other languages.
-
Open Questions, Observations and Other Comments
In each evaluation model or template, we can also add open questions or spaces for comments and observations linked to a specific group of indicators, or in an independent group. These free-text fields allow evaluators to provide detailed and contextualized responses about the individuals being evaluated. Open questions encourage deeper reflection and provide a richer and more comprehensive understanding of employee performance: by describing specific situations and observable behaviors, they provide context that helps us illustrate the employee's competencies and areas for improvement more clearly.
3.2 Step 2: Choosing which performance appraisal methodology to use
The second step involves determining, for each job position, which evaluation methodology we will employ: 90, 180, 270, or 360 degrees. When crafting your evaluation, you can also decide on the importance (weight %) assigned to each participating role.
Depending on the type of indicators under assessment, we can identify the most suitable roles to measure them. Naturally, we can select different methodologies based on each job role's unique characteristics. For example, it might be essential to gauge the team's perception of their Director (270 degrees), while for a Customer Service Manager, receiving feedback directly from clients (360 degrees) might be more pertinent.
Conversely, if we are evaluating numerical KPIs, employing a multi-perspective technique may not be necessary. If we tie achievement to specific metrics like the number of clients acquired or the number of completed projects, the answer is clear-cut and doesn't necessitate subjective interpretations for comparison.
The key lies in understanding our objectives when initiating performance evaluation processes. We shouldn't be overly concerned about the complexity of employing one model over another, as a digitized system can automate this management, delivering real-time results without the need for time-consuming bureaucratic procedures
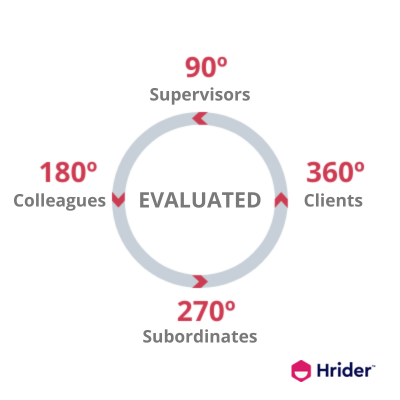
90º performance evaluation modality
In a 90-degree performance evaluation, the evaluation of the employee is conducted by their Supervisor.
The assessment provided by our manager is crucial for the development of the tasks assigned to us. They are responsible for establishing the mechanisms that guide our professional career plan and, additionally, they are the individuals who offer the feedback necessary for us to understand our strengths and weaknesses.
180º performance evaluation modality
In a 180-degree evaluation, Peers also participate as evaluators of an employee.
Often, our boss forms an impression of us based on our interactions with them or the final outcomes of our work. However, in our day-to-day responsibilities, we collaborate with our colleagues—sharing responsibilities, opinions, information, and approaches to tasks (Peer review). These colleagues, who share similar roles and objectives, can provide valuable insights into our areas of excellence and areas where we can make improvements.
270º performance evaluation modality
In a 270-degree performance evaluation, Subordinates (individuals led by a team leader) provide their assessment of their Supervisor's performance.
Offering feedback about our boss (Upward review) is something that we often do informally and may even share with many members of our organization, right? However, when we provide a constructive and respectful perspective through a formal mechanism, it not only benefits our Supervisor but can also enhance our professional relationship. Of course, we can maintain anonymity in this process, allowing team members to express their assessments comfortably.
For senior management, gaining insights from middle management employees' opinions helps in promoting successful leadership styles and identifying issues that might otherwise remain unresolved at the supervisory level.
360º performance evaluation modality
In a 360-degree professional performance evaluation methodology, we aim to gain a comprehensive perspective from all those who interact with a professional: Boss, Colleagues, Subordinates, and additionally, Clients and/or Suppliers.
Determining the degree of performance of a behavior is more subjective than calculating the achievement of, for example, a sales target where success is determined by a specific numerical value.
How can we arrive at an objective conclusion when the variables we assess are largely subjective? The more subjective data points we have, the more objective the final result becomes.
Consider the valuable insights that knowing what clients think of our work can provide to an organization!
Our goal is to improve our service for them continually, so why not give them a voice to guide us on the right path?
It's essential to remember that we don't only serve external clients; we often work for other departments within the company—these are our "internal clients"—who can also evaluate how we carry out our responsibilities.
Self-assessment
The employee's self-perception of their work remains a focal point in the job performance evaluation process. In addition to obtaining a 360-degree perspective from those who interact with the professional, we should also encourage employees to engage in self-reflection and provide their insights. Self-assessment is a highly advisable exercise that contributes significantly to the evaluation process. Moreover, it is one of the most valuable gifts we can provide to an employee for the advancement of their Career Plan.

3.3 Step 3: Generating the performance evaluation surveys
After designing the evaluation, the next step involves determining who evaluates whom. This can be a labor-intensive task unless you have a system that automates the creation of all surveys. For instance, in a 360-degree evaluation, each evaluated individual may receive at least 6 or 7 surveys to complete, and you need to multiply this by all the employees in your company!"
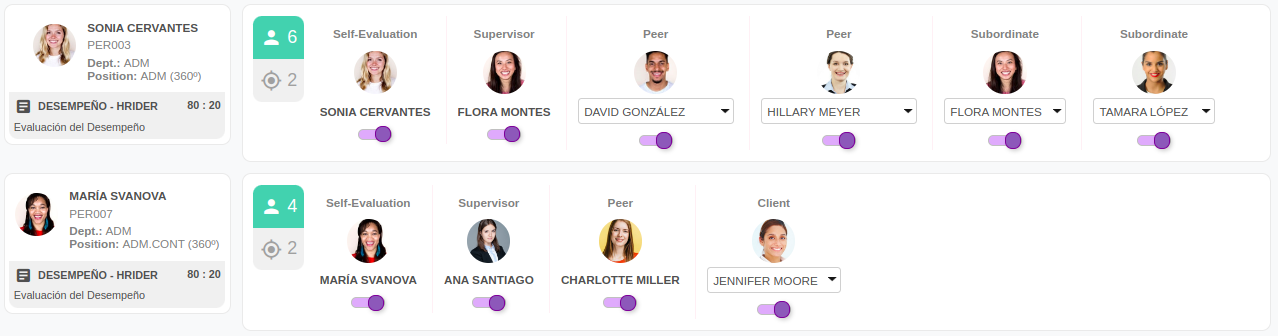
3.4 Step 4: Send out surveys and follow up on the performance appraisal process
One of the most challenging aspects of the evaluation and feedback processes is the significant administrative burden associated with tracking and performing calculations to generate reports. Therefore, it is vital to have an efficient system that enables full automation and delivers real-time information, reducing the need for manual efforts to analyze the results and make decisions.
This approach allows you to send reminders to participants whenever necessary, permit participants to modify their responses if needed, and monitor the progress of the process at any given time.
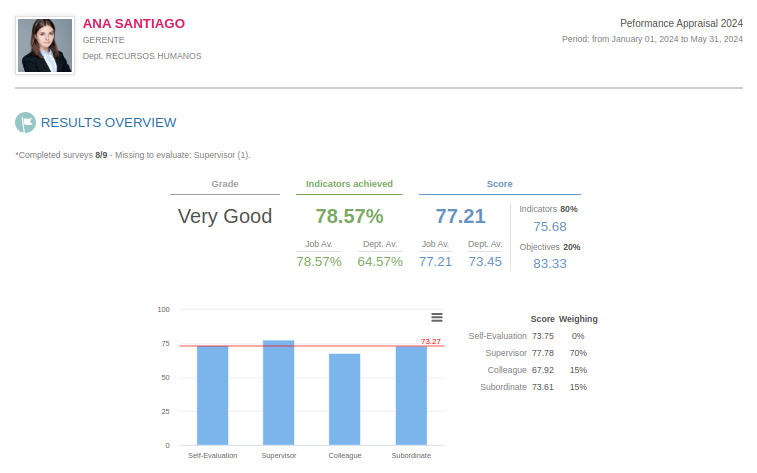
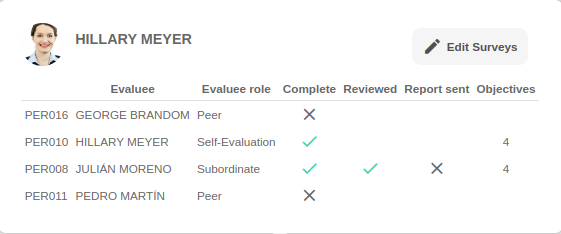 3.5 Step 5: Analyze the results
3.5 Step 5: Analyze the results
And we've arrived at the final step. After the surveys have been completed, we move on to collecting and analyzing the results, both at a global level and individually. This process provides the opportunity to meet with each person who was evaluated to provide and receive feedback with the results on the table. Offering ongoing constructive feedback is one of the best opportunities for professional development for an employee.
Additionally, with Hrider's Talent AI, your reports will include a semantic analysis of employees’ comments and responses to open questions.
With its high level of specialization in the field of human resources, our Artificial Intelligence offers a new paradigm in organizational communication analysis, providing a new, often hidden perspective on employees’ needs, desires, strengths, and areas for improvement within an organization.
Semantic analysis allows us to create a knowledge database that can be used for multiple use cases, from listing and classifying responses to generating training plans, obtaining the organization's competency database, investigating the causes of a negative work environment, detecting what we are doing well, identifying key elements, and more.
The use cases are vast, and the knowledge about our organization will help us make better decisions and establish effective, data-driven strategies.
4. Tips to succeed in your Performance Evaluation
Communication is necessary
Properly communicating how and why the organization conducts these assessments is essential. This serves a dual purpose: it motivates employees and makes them feel valued, thereby increasing their commitment. Additionally, it helps mitigate any fear or uncertainty regarding being judged by clarifying that the goal is to understand their needs and assist in their growth within the organization. It's also vital to be clear and precise when defining the indicators to avoid misunderstandings.
Less is more
While it's true that more information can lead to more insightful reports, let's face it: employees are unlikely to dedicate their attention to a survey, especially if there are multiple ones, with dozens of questions. This approach would yield results that don't accurately reflect the reality we aim to understand. It's wiser to be selective and choose the most critical indicators aligned with the organization's strategy.
Action oriented
Consistency with the organization's strategic initiatives is key. Imagine if all our employees enthusiastically participate in evaluations, but the organization fails to capitalize on this by developing action plans that address their needs. Employees will become disillusioned, viewing it as wasted time. This not only damages the organization's Employer Branding but also discourages participation in future evaluations. We have a dedicated post that delves into how to respond to evaluation results.
Flexible Sending
Flexibility is key, and with Hrider you have more options than ever to share and distribute your evaluations. In addition to automated sending, you can use the evaluation access URL. Generate a unique link for each evaluation that you can publish or share anywhere. It's ideal for use on internal networks, in messages, or in team communications. The user can access that URL to request that the invitation link be sent to them to access their survey. With the code we provide, you can embed the login form, integrating it directly into your company's website.
5. Examples and Templates
To facilitate the implementation of evaluation processes in your organization, we have compiled a series of downloadable templates that will allow you to effectively assess various aspects of performance. Below, you will find links to download the templates corresponding to each category:
-
Performance Appraisal: This template will help you conduct structured evaluations of your employees' performance. Download template
-
Feedback 360: Use this template to gather feedback from multiple sources and obtain a comprehensive view of an individual's performance. Download template
-
Organizational Culture: Understand how employees perceive the company's culture. Download template
-
Internal Communication: Assess the effectiveness of communication strategies within your organization. Download template
-
Intrapreneurship: Encourage internal innovation with this template designed to evaluate intrapreneurship projects. Download template
-
Onboarding: Ensure that new employees have a successful start with this template to evaluate your onboarding process. Download template
-
Exit Interview: Collect valuable feedback from employees who are leaving the company. Download template
-
Potential: Identify the growth potential of your employees to plan future developments. Download template
-
Training Needs: Discover the areas where your employees need more training and development. Download template
-
Leadership: Evaluate the skills and performance of your leaders. Download template
-
Remote work: With this template, you can assess the effectiveness of remote work and employee satisfaction with this mode. Download template
-
VUCA: In this template to assess the VUCA environment, you will find competencies to evaluate skills such as flexibility, planning, critical thinking, or resilience. Download template
Each template is designed to be intuitive and easy to use, ensuring that you can quickly implement these processes in your organization to continually improve talent management.
6. Conclusion
We have now reviewed all the necessary steps and provided some tips for conducting a successful performance evaluation:
-
Clearly communicate the purpose of this initiative.
-
Define the type of indicators (Hard/Soft Skills, Objectives/KPIs, Organizational Values, Languages, etc.) with clear and precise descriptions and weights based on your strategy.
-
Choose the appropriate evaluation modality (360º, 270º, 180º, or 90º feedback, with or without self-assessment).
-
Assign evaluators, launch surveys, and analyze the results.
-
Develop action plans based on these results.
As we've seen, this process can become quite complex, both in terms of its setup and the volume of data it generates. This is why manual methods or Excel alone are not suitable for handling it efficiently. Specialized systems that can automate the entire process while offering a high degree of customization are essential.
If you want to learn more and explore other important aspects, not just technical ones, that you should consider when conducting a performance evaluation, we've provided a selection of articles for you here:
7. Quiz: How much do you know about Performance Evaluation?